IoT Gateway: Overview & Role In Digital Transformation


The Internet of Things (IoT) concept was coined in 1999 when Kevin Ashtong proposed putting radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips on products to track them through a supply chain. Nowadays, this technology is becoming more and more mature, and people are trying to find practical solutions to implement it in different industries.
They came up with numerous intriguing small-sized IoT projects like gas leakage detectors or an intelligent anti-theft system. They also brought to life huge solutions for industries and manufacturers like smart agriculture (hello, drones and solid monitoring sensors) or the most well-known IoT concept: smart cities.
Nowadays, this technology is blossoming:
- According to Global Market Insights, the IoT gateway devices market size is projected to increase 15% annually to $16 billion by 2026.
- According to Statista, the global IoT industry revenue will reach over $1 trillion by 2030.
- According to the 2021 White & Case Annual Review, Saudi Arabia is constructing four smart cities: NEOM, Qiddiya, the Red Sea Project, And Amaala.
- According to Fortune Business Insights, the major market players are AT&T, Cisco Systems, Siemens AG, and Oracle Japan.
The article contains a comprehensive description of one very important component of the Internet of Things system: a gateway. The language of the article is easily understandable by people with any level of technical expertise. Tech-savvy specialists, in turn, can find a list with links to more technical texts at the end of the article.
Enjoy reading!O
What Does IoT Stand For
Firstly, let’s define the technology itself.
The Internet of Things is a network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data with the system core (called cloud) and one another through the Internet.
This technology empowers businesses in multiple industries like manufacturing, retail, logistics, supply chain, healthcare, and many more. We have various articles on these topics in our blog. Here I want to focus on the general benefits of the Internet of Things.
Benefits of the Internet of Things
While different industries leverage IoT for specific benefits, several overarching advantages are universally applicable. In this abstract, we explore these generic benefits.
- Enhanced efficiency – the Internet of things enables automation and remote monitoring of devices and processes, leading to increased efficiency in operations. For example, in manufacturing, smart sensors can track equipment performance in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Improved decision-making – with access to real-time data from connected devices, businesses can make informed decisions quickly. Advanced analytics provide valuable insights into customer behavior, operational performance, and market trends, enabling organizations to respond promptly to changing conditions and optimize strategies.
- Cost savings – by streamlining processes, reducing waste, and optimizing resource utilization, the Internet of things helps businesses cut costs. For instance, in agriculture, IoT-enabled precision farming techniques can minimize water usage, fertilizer application, and energy consumption, resulting in significant savings.
- Enhanced customer experience – the Internt of Things enables personalized and responsive customer experiences. For example, in retail, smart devices such as beacons and smart shelves can deliver targeted promotions and recommendations to shoppers based on their preferences and location, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased safety and security – interconnected systems can enhance safety and security in various environments. For example, in smart homes, smart devices can detect and alert residents to potential hazards like smoke or carbon monoxide leaks. In industrial settings, connected surveillance cameras and sensors can monitor for intrusions or safety hazards, helping prevent accidents and unauthorized access.
And the Internet of Things gateway is a significant part in bringing these benefits to live.
What Is The Internet of Things Gateway
The Internet of Things gateway is a device compact in size and encased in a robust plastic housing that transmits information from smart devices to the cloud. Usually, it happens through Wi-Fi, but the transfer method varies depending on the particular Internet of Things architecture.
Example: A Cellular Gateway
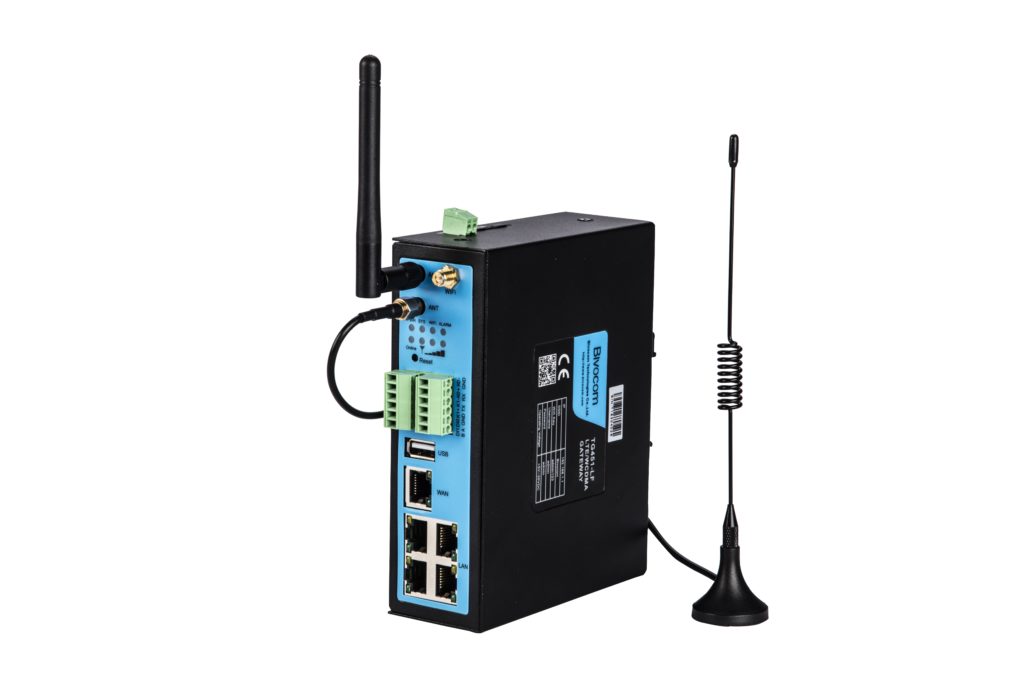

A cellular gateway is a device that enables communication between devices or sensors in remote locations and a central server or cloud platform using cellular networks. It acts as a bridge, allowing data from devices equipped with cellular connectivity to be transmitted over the internet to a designated server.
Cellular gateways are commonly used in applications such as industrial IoT, smart agriculture, asset tracking, and environmental monitoring, where traditional wired or Wi-Fi connections may not be feasible or reliable. These gateways typically support multiple cellular technologies like 4G LTE, 5G, and NB-IoT, providing flexibility and coverage options for various deployment scenarios.
The IoT gateway has various characteristics like:
- Processor
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Supported Wireless Connections
- Security modules
- Operating system
- And much more specific technical characteristics like I/O, GPIO, form factor, etc.
All data in the system runs through these small boxes. But how does it work?
How The IoT Gateway Works (On The Real-Life Example)
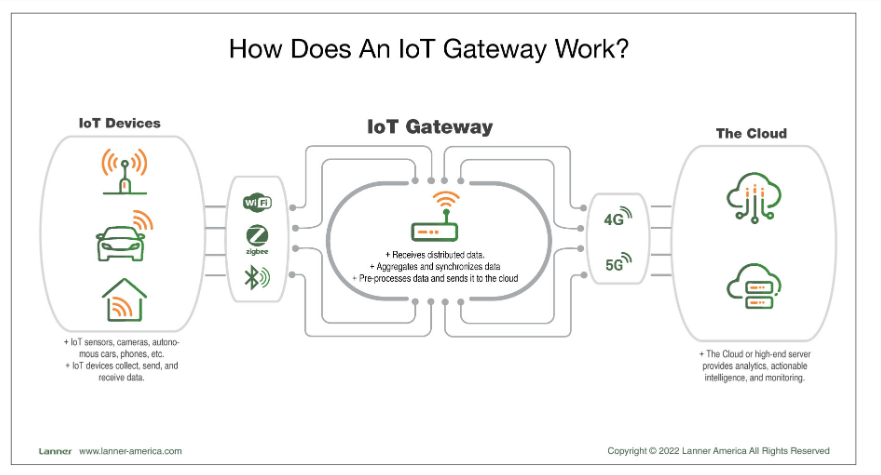
Let’s examine the IoT gateway with the real-life use case of an IoT system with fridge sensors. It monitors the work of commercial refrigeration online.
Every refrigerator comes with a bunch of sensors that gather information like temperature, humidity, door status (closed/open), video, etc. Every sensor comes with a microcontroller responsible for data capture and transfer. Together, the sensor and microcontroller form a sensor node (however, it’s often called just a “sensor” for simplicity).
A sensor node isn’t supposed to operate with the data locally, so it should pass the data to the cloud. So all sensor nodes use Low Power Short-Range Communication Protocols ZigBee to transmit the data to the gateway. Here the datastreams are aggregated, processed, and then passed further to the cloud through Ethernet (in some cases with moving sensor nodes, it could be 5G or 4G).
Small note: Theoretically, sensor nodes can connect to the cloud directly through Ethernet, but it’s not the optimal solution. Ethernet connection implies that every sensor should possess enough power capacity (which is a rare case for sensors) and appropriate equipment (even rarer case).
We have already mentioned some IoT gateway functions like data transfer, processing, and aggregation. But let’s take a closer look at all of them.
Key Functions Of The Internet of Things Gateway
Function #1: Communication With The Cloud
It’s the key role. The gateway connects the sensor layer and the cloud, using Wi-Fi, 4G, or 5G. The communication is bilateral: the raw data from devices goes to the cloud and commands go in the opposite direction.
Why it matters:
- Smart devices that don’t support the internet connection can get it with gateways
- Centralized dataflow control
- Monitoring the Internet of Things fleet
- It gives remote control over the the fleet
Function #2: Route the Traffic

The gateway operates as a router by managing the traffic flow.
Why it matters:
- Centralized traffic management easier to control and analyze
Function #3: Support of multiple transfer protocols
Sensors use different low power short-range communication protocols such as Bluetooth Low Energy, ZigBee, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), LoRaWAN, or medium-long range protocols like Wi-Fi, LoRa.
The gateway, in turn, transfers the data through more power-intensive protocols like cellular wireless/LTE, and Ethernet. However, the gateway should support all protocols to ensure communication.
Why it matters:
- All things speak in different languages. The gateway facilitates communication inside the Internet of Things network
Function #4: Isolation of sensor nodes
Since the gateway becomes the only access point to smart devices, sensor nodes become isolated from the public Internet.
Why it matters:
- The gateway becomes a firewall for sensors by not allowing direct connection to them.
Function #5: Aggregation and preprocessing of the data (edge computing)
The gateway may have the local processing power to aggregate, filter, summarize, and cluster gathered data before passing it further. There are also options to configure the gateway to handle some typical issues and provide instant responses to the smart devices.
Why it matters:
- It reduces the overall dataflow
- Lower data transmission costs
- Improved response time to the smart gadgets
Function #6: Security
Smart devices often demonstrate low-security levels. Security challenges top the list of the Internet of Things trends in 2022. Gateways become an effective solution here, coming with essential security mechanisms like TPM 2.0, advanced encryption, unauthorized access control.
Why it matters:
- Improved security
- Prevent the diversion of sensitive data during transfer
- Prevent the unauthorized connections outside the Internet of Things ecosystem
Function #7: Local storage of data
Gateways feature enough local storage capacity to cache data when they are disconnected from the cloud.

Why it matters:
- All measurements remain safe and sound
Software for the Internet of Things Gateways

The Internet of Things systems often require complex custom software solutions. The larger the application, the more complicated update management, fleet management, maintenance, and other operations become. The development of software for gateways in the Internet of Things also requires huge expertise since all functions in the abstract above should be well-thought-out and carefully implemented.
Fortunately, there are a lot of software providers on the market. A list with some of them:
Custom solutions:
- SumatoSoft – builds web and mobile custom Internet of Things solutions. Their services include the development of edge processing and analytics products.
- Wind River – the company that deliver software for intelligent connected systems.
OS:
- Contiki – the OS for Next-Generation Smart Devices
- Bosch Suite – the company provides the backbone to the Internet of Things projects.
- Agile IoT – is a modular hardware and software for a cellular gateway.
Open-source solutions:
- Foghorn – is a lightweight edge Internet of Things platform.
- Eclipse Kura – is an extensible Edge Framework.
Some Specific Gateways Types Inside the Internet of Things

Industrial Internet of Things Cellular Gateways
The Industrial Internet of Things (aka IIoT) is geared toward durable devices since industrial operations (for example, manufacturing) usually implies dealing with hostile environments like high temperatures, increased dust levels, nonstandard humidity levels, etc.
It’s also expected from sensor nodes to have long battery life and be rugged enough to withstand the impact of occasional hits. Another requirement is energy-efficient communication networks. All these additional challenges should be addressed during the manufacturing of cellular gateways and sensors for the Internet of Things.
Here we want to list some hardware manufacturers. There are many more.
- Eurotech – the company offers ready-to-use devices that help innovate customers’ enterprise business models.
- Dell – the company is focused on producing Gateways to withstand harsh industrial conditions.
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise – provides ruggedized edge compute solutions that acquire, analyze, and act upon edge data in the harshest environments.
- Cisco – has several series of smart devices that simplify asset and facility monitoring as well as preventive maintenance.
More vendors:

Vehicle Gateways
This type is integrated into moving units like vehicles (that is how the name came). The way they affect our day-to-day life is considered in the next section. However, the biggest contribution here lies in the way vehicle gateways have changed the supply chain and transformed logistics. It became possible to get precise, real-time location even in challenging geographical surroundings! They also have a direct bearing on engine diagnostics, fuel efficiency, driver productivity, and safety. They brought to life such a concept as digital twins which is impossible to overestimate when dealing with highly expensive equipment (like aircraft engines).
Internet of Things Gateways: Usage Examples
Example #1: Real-Time Monitoring of Industrial Refrigerators
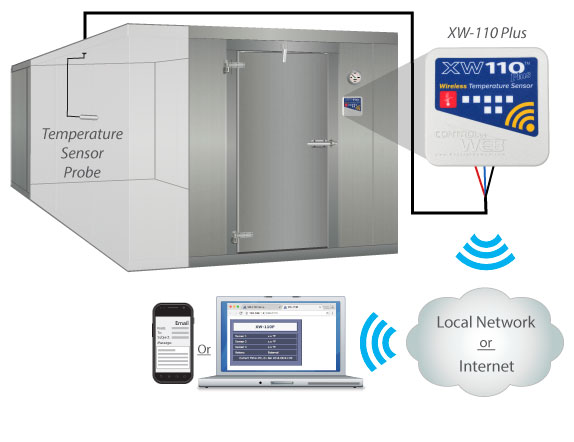
Challenge:
This system is about monitoring multiple indicators in the industrial refrigerators, visualizing the gathered data and its management. Besides the technical complexity of the solution, let’s highlight the part we need: gathering of the information.
Sensor nodes that monitor industrial refrigerators should handle really low temperatures. Direct internet connection of sensors with the 4g in such a harsh environment isn’t the optimal decision.
The gateway role:
The cellular gateways gather the data from sensors with low-range protocols and then pass it to the cloud. Since they are placed outside the harsh environment, the need to handle low temperatures disappears. Simple and smart.
Example #2: Carsharing – Locking and Unlocking Car With the Phone
Challenge:
Nowadays, software vendors offer video surveillance solutions with excellent HD image quality. It would be impossible without gateways that preprocess, filter, and compress data.
For example, it took 340 cameras that worked 24/7 to secure a 19.000 meter square with 1354 apartments, parking lots, a hallway, and front gates. The system produces tons of records that should be stored and analyzed somehow.
The gateway role:
We have mentioned that gateways may come with additional computing capacity to preprocess the data. That’s it! Thanks to edge computing, the video footage is automatically analyzed locally. Thus the system doesn’t store useless records (for example, of unoccupied areas).
Example #3: Video Surveillance System With Tons of Recorded Data
Challenge:
Nowadays IoT vendors offer video surveillance solutions with excellent HD image quality. It would be impossible without IoT gateways that preprocess, filter, and compress data.
For example, it took 340 cameras that worked 24/7 to secure a 19.000 meter square with 1354 apartments, parking lots, hallway, and front gates. The system produces tons of records that should be stored and analyzed somehow.
The IoT gateway role:
We have mentioned that IoT gateways may come with additional computing capacity to preprocess the data. That’s it! Thanks to edge computing the video footage is automatically analyzed locally. Thus the system doesn’t store useless records (for example, of unoccupied areas).
Example #4: Flower Kiosk With 4g Connectivity

Challenge:
It’s quite simple today to purchase flowers 24/7 thanks to an automated self-service retail delivery system. This solution has an API that should be able to link to almost any POS, Website, or Mobile App. How?
The gateway role:
Thanks to the gateways with secure standards for communication through 4G technology! This solution can be easily distributed since the kiosk works as a self-sufficient, secure unit.
Case-study link
We also want to examine one additional case – business communication and the role of the Internet of Things here.
How Has the Internet Improved Business Communication Worldwide? Select Three Options
Instant Communication
The Internet enables real-time communication through email, instant messaging, and video conferencing, allowing businesses to connect with clients, partners, and employees instantly, regardless of geographical location. This immediacy enhances collaboration, speeds up decision-making processes, and facilitates swift resolution of issues.
Global Reach
The internet has eliminated geographical barriers, enabling businesses to reach a global audience easily. Through websites, social media platforms, and online advertising, companies can promote their products or services to potential customers worldwide, expanding their market reach and opportunities for growth.
Cost Efficiency
Compared to traditional communication methods like postal mail or international phone calls, internet-based communication is significantly more cost-effective. Businesses can save money on postage, printing, and long-distance calling charges by utilizing email, VoIP services, and messaging apps for communication, leading to substantial cost savings in the long run.
Building The Internet of Things System With SumatoSoft
SumatoSoft, a software development company, delivers custom software solutions and services to established and young companies that need tailored software for further growth.
One of the key areas of competence is custom Internet of Things software development for startups, enterprises, and middle businesses. The competence derives from 10 years of experience in the market of IoT design services and 150+ developed projects.
Thanks to the 4.8 rating on the clutch platform, we stay sure that our software works great and delivers business value. If you plan to implement the Internet of Things network with gateways, get in touch with us and get a free quote!
- Whitepaper: What is IoT Architecture
- Guide: IoT Update Management
Key Takeovers
- A gateway is a physical device that looks like a plastic box with sockets
- It connects sensor nodes and the cloud through Ethernet or cellular networks
- There are 7 key functions of gateways inside the Internet of Things ecosystem. They are:
- Communication With The Cloud
- Route the traffic
- Support of multiple transfer protocols
- Isolation of sensor nodes
- Aggregation and preprocessing of the data (edge computing)
- Security
- Local storage of data
- Industrial Internet of Things systems exist in a very hostile environment that requires Industrial sensors and gateways to be more rugged
- One of the best Internet of things custom software providers is the SumatoSoft company
Thanks for reading!
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us info@sumatosoft.com