Custom CRM Development: How We Build Enterprise CRMs


Did you know that companies with fully utilized CRM systems can increase their sales by up to 29%?
It’s official statistics reported by Salesforce.
A well-implemented CRM system can transform medium and large businesses. In the enterprise realm, CRM helps to reach strategic goals: foster customer loyalty, streamline sales processes, and deliver personalized customer experiences at scale. As a software developer at SumatoSoft, I develop custom enterprise software solutions tailored to the expansive needs of medium and large businesses. In this article, I want to share insights and knowledge on how to build a custom CRM system, with a particular emphasis on large-scale operations typical of enterprises.
Developing a CRM: From integrated modules to custom development
Enterprises have 3 paths to consider: CRM module, buy off-the-shelf CRM, and build a custom CRM. I’ll go from the easiest way to the most complex and costly. Go from top to bottom, moving to the next scenarios if finding previous ones inappropriate.
Below is an overview of these scenarios.
Decision summary: “Build vs Buy vs ERP Module”
| Decision factor | ERP CRM module | Buy off-the-shelf CRM | Build custom CRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best fit when | CRM must be tightly coupled to finance / ops / supply chain | CRM is a supporting system with standard sales processes | CRM is a core business system and a competitive differentiator |
| Time to first value | Medium (depends on ERP rollout & customization) | Fast (weeks to 2-3 months) | Medium (3-6 months for MVP) |
| Customization depth | Medium; constrained by ERP data model | Limited to platform constraints | Very high (process-driven, domain-specific) |
| Scalability & flexibility | Scales with ERP; flexibility decreases over time | Scales well within vendor limits | Designed for your scale and future evolution |
| Integration complexity | Low inside ERP, high outside it | Often increases with customization | Optimized for your ecosystem (ERP, data, legacy) |
| User adoption | Often lower due to ERP UX complexity | Mixed; depends on configuration quality | High when tailored to real workflows |
| Data ownership & control | ERP-dependent | Vendor-dependent | Full ownership and architectural control |
| Compliance & security | Inherits ERP compliance model | Depends on vendor capabilities | Fully designable to regulatory needs |
| Vendor lock-in risk | High | High | Low |
| Initial cost | Medium | Low to medium | Medium to high |
| Long-term TCO | Grows with ERP customization & upgrades | Grows with licenses and add-ons | Predictable, optimized over time |
| Typical business risks | Rigid processes, slow change cycles | Over-customization, rising license costs | Under-scoped discovery, weak governance |
Scenario 1: Utilizing an ERP’s built-in CRM module
This scenario involves activating and using the CRM module already present within your ERP system. It’s the most straightforward approach, leveraging the ERP’s inherent capabilities to manage customer relationships without the need for external integration. It could be a SaaS ERP or on-premise.
Here are well-known ERP systems that offer a CRM module:
- SAP S/4HANA;
- Oracle NetSuite;
- Microsoft Dynamics 365;
- Sage 300;
- Infor CloudSuite CRM;
- Epicor ERP;
- Acumatica Cloud ERP;
- SYSPRO ERP.
If you have one of them, lucky you are. Contact your account manager and ask about the opportunities and terms of connecting a CRM module to your current system.
When referring to:
- the enterprise is already leveraging an ERP system;
- the need for a CRM solution has become urgent;
- you’re content with the performance and capabilities of your current ERP system.
What you will get:
- the opportunities of the CRM module of the ERP vendor;
- unified, consistent and accurate data;
- quick and guided setup process;
- the same touch point of communication regarding any issues – your account manager;
- reduced complexity in IT infrastructure and management thanks to a single software vendor.
Limitations:
- feature set confined to the vendor’s CRM capabilities;
- potential lack of niche features, such as advanced AI-driven insights or industry-specific functionalities, limiting tailored CRM strategies.
- dependence on a single vendor for both ERP and CRM functionalities, which could pose risks if the vendor’s solutions do not keep pace with industry advancements.
Cost:
- Development and customization: minimal to none
- Integration: negligible
- Subscription fees: depend on the ERP vendor’s pricing model, but lower than acquiring a separate CRM system.
- Training and support: some costs that may be partially covered under the existing ERP support package.
- Data migration: low to none
- Infrastructure: no additional infrastructure costs
Scenario 2: Integrating an off-the-shelf CRM with existing ERP
This scenario entails choosing a standalone CRM solution from the market and integrating it with the current ERP system. It allows enterprises to select a general CRM or an industry-focused CRM with specific features tailored to their customer relationship management needs. Here is a brief list of the most well-known general and focused CRMs with industries they serve:
- HubSpot – general, manufacturing, marketing
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 – general, finance, retail, manufacturing
- NetSuite – general, eCommerce, wholesale distribution
- Salesforce – general, healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing
- Zendesk – customer service across various industries
- Pipedrive – general, manufacturing, sales-focused businesses
- Freshsales – general, with a strong focus on sales automation and contact management
- Infor CRM – general, manufacturing, distribution
- Zoho CRM – general, real estate, retail, finance
- Oracle’s Siebel CRM – healthcare, finance, automotive, consumer goods
- SAP Customer Experience (formerly SAP C/4HANA) – retail, manufacturing, professional services
- Propertybase – real estate, with a focus on real estate agents and brokers
- Amadeus Hospitality CRM – hospitality, specifically designed for hotels and the travel industry
When referring to:
- regardless of whether the enterprise currently utilizes an ERP system;
- the enterprise requires some industry or niche-specific set of functionalities;
- the enterprise has to comply with some specific regulations, such as patient data management in healthcare or laws and regulations in finance.
- you have time and budget to find the optimal CRM solution and integrate it with inner systems.
What you will get:
- a CRM with a diverse set of features;
- the ability to choose a CRM perfectly aligned with your business requirements;
- round-the-clock support and maintenance from external providers;
- pricing that adjusts to your needs, varying by user count or other vendor-specific criteria;
- scalability that accommodates user growth and the addition of new functionalities;
- immediate access to the newest technologies like AI and Voice Assitance, deployable with just a few discussions with an account manager.
Limitations:
- excessive features can complicate operations without adding clear value.
- the system may lack the flexibility needed for some business processes.
- difficulties can arise when linking with older or bespoke ERPs.
- initial attractive prices can quickly escalate with the addition of necessary customizations, integrations, and scaling opportunities.
- moving customer data can be challenging, with risks to data integrity.
Cost:
- Development and customization: serious customization costs since the vendor isn’t familiar with your business.
- Integration: negligible in case the vendor provides integration with your ERP system, and significant if the integration is absent.
- Subscription fees: depend on the ERP vendor’s pricing model, but are higher than the first scenario. These fees often escalate quickly after implementing the CRM (see limitations).
- Training and support: low because vendors often have comprehensive learning resources and may offer webinars and training, sometimes at an additional cost or as part of their services.
- Data migration: from low to high depends on the integration options. Without integration, the migration could be complex and incur costs for larger datasets.
- Infrastructure: if the CRM is cloud-based, additional infrastructure costs might be minimal, but on-premise solutions could require new hardware or upgrades.
Scenario 3: Developing a custom CRM
This scenario involves the development of a CRM system following the general process of custom software development: requirements gathering, design, development, testing, integrating, deployment, and training. It represents a solution designed from the ground up to fit unique business processes, offering unparalleled customization and flexibility.
When referring to:
- regardless of whether the enterprise currently utilizes an ERP system;
- the enterprise seeks functionalities that are not available in off-the-shelf CRM solutions.
- the enterprise has to comply with some specific regulations, such as patient data management in healthcare or laws and regulations in finance.
- the enterprise is ready for long-term custom development in about one year.
- the business requires a CRM that can evolve with its changing needs and scale accordingly.
What you will get:
- a CRM built to match exact business requirements, workflows and processes.
- the potential for perfect integration with the existing ERP and other systems.
- high levels of customization and scalability that are agreed upon even before the development starts.
- direct control over the development and future enhancements of the CRM system.
Limitations:
- custom CRM development requires high upfront costs, encompassing everything from design to deployment.
- longer development and deployment timelines.
- finding a trustful software provider is a challenging task.
Cost:
- Development and customization: significant, as the CRM is built to spec, involving detailed planning, design, and coding.
- Integration: potentially high, depending on the complexity of integrating the custom CRM with the existing ERP system and other business applications.
- Subscription fees: none.
- Training and support: some cost because custom training programs will need to be developed, and internal or external support structures established.
- Data migration: high based on the complexity and diversity of existing data.
- Infrastructure: additional infrastructure costs may be necessary, especially for on-premise deployments, to support the custom CRM system.
Key considerations for implementing CRM in your business
Okay, now I want to share our approach at SumatoSoft on what we did before developing a CRM for a Toyota car dealer.
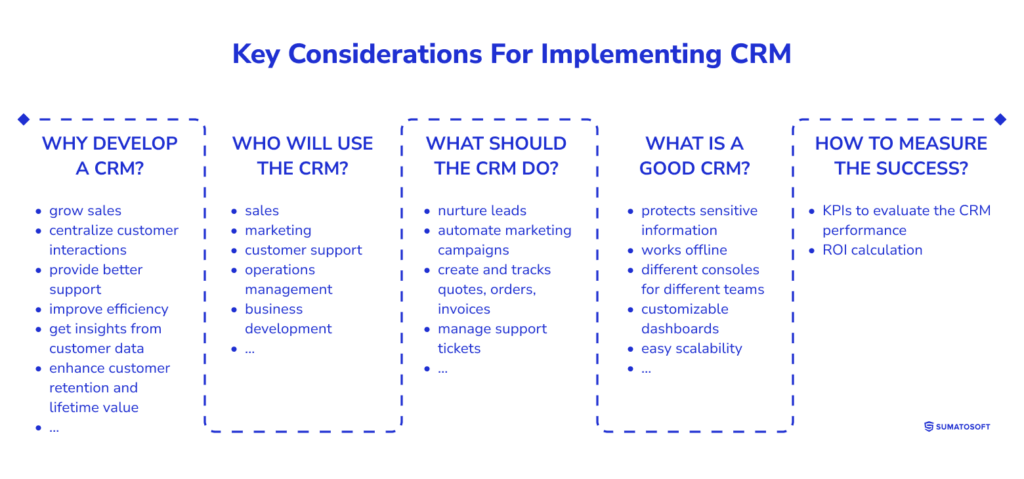
First of all, it’s necessary to ask several questions:
- Why develop a CRM?
- Who will use the CRM?
- What should the CRM do?
- What is a good CRM?
- How to measure success?
I know that these questions might seem unusual, but this approach allowed us to develop a CRM that was deployed across 40 facilities.
For simplicity, I displayed these questions and answer samples in the image. Think about this picture before moving on
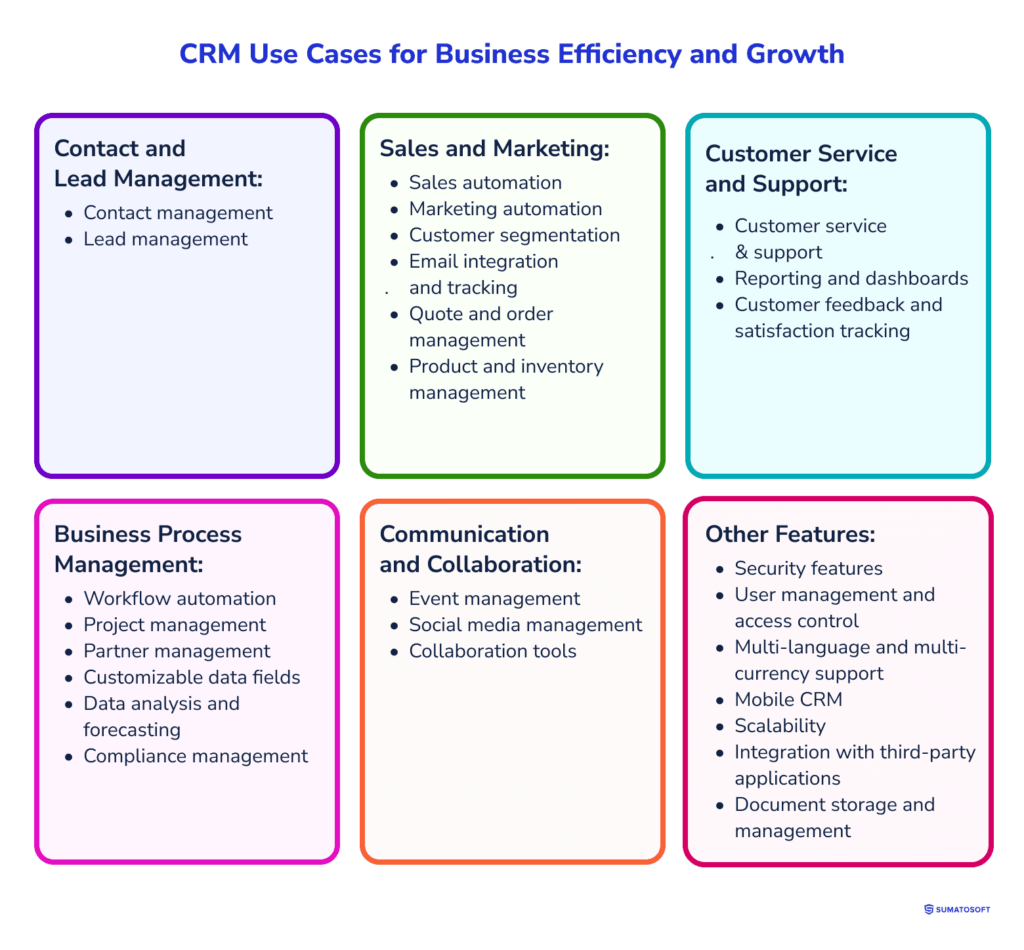
CRM use cases for business efficiency and growth
For medium and large businesses, a CRM system must cover a comprehensive range of use cases to manage customer relationships and support business processes effectively. Every use case corresponds to one or another advantage of software solutions for enterprises.
Here’s a list of critical use cases that an enterprise-level CRM should typically cover:
CRM implementation: overcoming challenges
Implementing a CRM system within a company with large-scale operations is a complex task, fraught with challenges. In this section, I would like to share the core challenges we face during Toyota CRM development as well as CRM development for our other Clients.

Challenge #1: Mapping complex operations to CRM functionalities
In large enterprises, CRM problems rarely come from missing features. They originate from real workflows that do not conform to standard CRM models.
In Toyota CRM development and other enterprise projects, we repeatedly saw the same pattern. The customer journey was fragmented across teams and systems. An inquiry entered through one channel, sales handled negotiations in parallel streams, pricing required custom approvals, billing lived in ERP, and post-sales support used separate tools. Each team tracked its part correctly. End-to-end visibility was missing.
Data capture wasn’t a problem, while data coherence was.
When we tried to force all operational details into CRM, the system became heavy and unusable. When we simplified the model, teams lost context and relied on spreadsheets and side tools. Both approaches led to low adoption.
The breaking point usually appeared when one CRM record had to serve different goals at once:
- Sales needed a clear pipeline.
- Finance needed accurate pricing and approvals.
- Service needed full interaction history.
A single rigid structure could not support all three.
How we handled it:
We started with how work actually happens, or so-called business process analysis.
We ran process walkthroughs with sales, finance, operations, and support to identify:
- Where are decisions made?
- Which data changes the outcome?
- Which information must stay in CRM, and which should remain in other systems?
Based on this, we built a process-driven CRM model:
- CRM stores customer state, interactions, and decisions.
- ERP handled pricing, contracts, and transactions.
- Integrations synchronized only the data that users actually needed.
As a result, CRM stayed usable for daily work while management gained a consistent customer view across departments.
Challenge #2: Change management and user adoption
CRM adoption fails quietly. The system works. The data looks fine. People keep using spreadsheets and email.
The second biggest challenge we faced across almost all enterprise CRM projects, including those related to Toyota. Sales teams were used to personal files, inbox threads, and informal notes. CRM required discipline: logging interactions, updating stages, relying on shared data. On paper, this looked reasonable. In daily work, it felt like extra effort.
Where does the problem lie?
Salespeople worried that CRM slowed them down, exposed unfinished deals, and forced them into someone else’s process. When CRM felt like reporting, usage dropped to a minimum.
The biggest risk appeared after launch. Training was completed, access was granted, and activity declined. CRM existed, but decisions were still made outside of it.
How we handled it
We treated adoption as a product problem, not a training problem.
First, we identified where CRM replaced existing habits and where it added friction. We removed steps that did not influence decisions and automated data capture wherever possible.
Second, we aligned CRM usage with real incentives:
- Pipeline reviews used only CRM data.
- Approvals and forecasts depended on the CRM state.
- Parallel reporting in spreadsheets was deliberately removed.
Third, we trained users on their workflows, not on CRM features. Sales learned how CRM helped them close deals faster. Managers learned how it reduced manual reporting. Support teams saw how context improved handovers.
Feedback loops stayed open after launch. We adjusted fields, flows, and dashboards based on real usage patterns.
CRM stopped being a system people had to fill in. It became the system that reflected how work was actually done.
Challenge #3: Data migration without breaking operations
Data migration is one of the fastest ways to damage trust in a new CRM.
In enterprise CRM projects, customer data is rarely stored in a single location. Sales history sits in legacy CRMs and spreadsheets. Support data lives in ticketing systems. Contacts and contracts are duplicated across databases. Some records are outdated, some incomplete, some contradict each other.
It’s really easy to lose some data. Even partially lost data leads to a significant risk – losing meaning.
When data is moved without context, CRM users lose trust in it. A deal shows the wrong status. A customer has multiple owners. Historical interactions disappear or appear out of order. When this happens, teams revert to old systems within days.
Another risk is continuity. Sales and support cannot pause work while data is being cleaned. CRM must remain usable during migration, or the rollout fails.
How we handled it
We never migrated everything at once.
We split migration into controlled phases:
- High-value, frequently used data first.
- Long-tail historical data later.
- Archived data kept accessible outside CRM.
Before migration, we defined ownership rules and conflict resolution logic. Duplicate records were resolved intentionally, not automatically. Fields that did not affect decisions were dropped.
Each phase followed the same cycle:
- Extract and transform a limited dataset.
- Validate it with business users.
- Run parallel checks against source systems.
- Only then make it active in CRM.
During migration, old systems stayed read-only. New work happened in CRM from day one. This avoided split usage and data drift.
As a result, users trusted the data they saw, and CRM became the single source of truth instead of another uncertain system.
We used this data migration checklist to ensure we stay on track during any data migration process.
Challenge #4: Defining success metrics
In several enterprise CRM projects, the same question surfaced right after launch:
“Is this CRM actually working?”
Usage was there. Data was there. Dashboards were built. Yet teams could not give a clear answer.
The reason was simple. Success was never defined upfront.
We often entered projects where different stakeholders expected different outcomes. Sales wanted better visibility. Management expected revenue growth. Operations looked for cleaner handovers. All of these expectations were valid, but none of them were translated into measurable criteria before implementation started.
As a result, CRM accumulated information without answering the main question: what changed after implementation.
How we handled it
We defined success metrics before implementation even started.
Together with business owners, we selected a limited set of KPIs that:
- Reflected real business outcomes.
- Depended on CRM data.
- Were already used in management discussions.
For every KPI, we defined which CRM signals supported it and how it would be reviewed. Dashboards were built only around these metrics.
During rollout, metrics were reviewed regularly. When results did not move, we adjusted processes and workflows. Reporting remained unchanged.
CRM effectiveness was evaluated through decision quality and workflow impact across teams.
Challenge #5: Calculating ROI
In enterprise CRM projects, ROI discussions usually start late and lead to frustration.
Finance expects a clear number. Delivery teams list improvements. Business owners feel the system helped, but struggle to prove it. As a result, CRM value is questioned even when the system is actively used.
We encountered this pattern multiple times. Direct costs were easy to calculate. Licenses, development, integrations, support. Benefits were harder. Revenue growth depended on many factors. Customer satisfaction was discussed qualitatively. Productivity gains were real, but scattered across teams.
Without a structured approach, ROI discussions turned subjective and lost credibility.
How we handled it
We defined ROI expectations before rollout and tracked them continuously.
We focused on three groups of indicators:
- Customer impact – we compared retention, repeat sales, and satisfaction metrics before and after implementation and linked changes to customer lifetime value.
- Productivity – we measured deal progression, case resolution speed, and workload distribution. Time saved was translated into additional capacity or revenue potential.
- Avoided costs – we tracked reduced churn, fewer manual corrections, and lower reliance on side tools.
ROI was reviewed over time as data matured. This produced numbers that business and finance teams accepted and used.
SumatoSoft’s way of developing a custom CRM
We developed a custom CRM for the Toyota car dealer, leveraging Ruby on Rails and Scrum methodology for quick development and integration. We focused on creating a CRM module that includes virtual desktops tailored for different employee roles, streamlining customer support and task management.
The CRM features an interactive UI and integrates with existing systems, automating sales and service processes, reducing costs, and improving customer retention. After the implementation of the CRM module many company’s processes of selling and servicing cars were automated, the company has reduced operational costs, hastened sales cycles and improved customer retention rates.
Some More Facts About SumatoSoft:
- We deliver custom enterprise software development services and build solutions like ERP, CRM, document management systems, and human resource management systems.
- We build software for multiple industries: various industries like eCommerce software, Elearning development, Financial software development, healthcare software development, Real Estate, Logistics software, Travel, and more.
- 60 specialists on board, 12 years on the market.
- 70% of our team is senior-level developers.
- We focus on long-term cooperation. 70% of our clients come back to us with another project.
- Thanks to our strong commitment to deadlines and their needs, our Client satisfaction rate is 98%.
- We are a member of The Council for Inclusive Capitalism;
- We are recognized as top software developers by leading analyst agencies like Techreviewer, Clutch, and Goodfirms.
- We only release the software if it meets the specified percentage of acceptance criteria. The percentage is agreed upon with you in the quality assurance strategy.
Get in touch with us for a free consultation. Let’s build a new product together.
SumatoSoft is great in every regard including costs, professionalism, transparency, and willingness to guide. I think they were great advisors early on when we weren’t ready with a fully fleshed idea that could go to market. They know the business and startup scene as well globally.
They did a great job hitting cost estimates and are a bargain for quality. They also helped our business concept greatly. We are confident in our plan and future in the hands of SumatoSoft.
Words from the author
In conclusion, my role as a software developer at SumatoSoft has allowed me to witness the transformative potential of a well-crafted CRM system in the enterprise world.
CRM systems allow to elevate sales, optimize operations, enhance customer experience, unlock new business opportunities, nurture loyal customers, boost brand reputation, and offer a multitude of other benefits.
Embracing CRM integration can be a challenging journey, one that I wholeheartedly recommend for every enterprise to embark upon.
If you need a CRM, feel free to get in touch with the company I’m working on!
FAQ
How long does custom CRM development take for an enterprise?
For enterprise-scale custom CRM development, the timeline typically ranges from 3-6 months to reach a working MVP and 9-18 months to achieve a stable, fully adopted system.
The timeline depends less on technology and more on:
- Clarity of business processes.
- Number of integrations.
- Data migration scope.
- Decision speed on the Client side.
Projects slow down when discovery is rushed or ownership is unclear.
What is the cost range and main cost drivers?
Enterprise custom CRM projects typically range from $150,000 to $1M+.
Main cost drivers:
- Number and complexity of integrations.
- Data migration and data quality work.
- Security, compliance, and audit requirements.
- Workflow automation and approval logic.
- Reporting and analytics depth.
Licensing costs may be lower than off-the-shelf CRMs, while delivery and integration costs are higher upfront.
Which modules belong in MVP vs Phase 2?
MVP usually includes:
- Accounts and contacts.
- Leads or opportunities.
- Activity tracking.
- Basic workflows.
- Roles and permissions.
- Core reports.
Phase 2 typically adds:
- Advanced automation.
- Complex approvals.
- Deep ERP integration.
- Analytics and forecasting.
- Partner or multi-channel flows.
- AI-driven insights.
MVP should support daily work. Phase 2 should optimize and scale it.
How to integrate CRM with ERP safely?
Safe integration starts with clear system boundaries.
CRM should handle customer state, interactions, decisions.
ERP should handle: pricing, contracts, invoicing, transactions.
Integration should synchronize only necessary data, use stable identifiers, and include monitoring and retry logic. Event-based or asynchronous patterns reduce coupling and failure impact.
How to plan data migration and ensure data quality?
Start with ownership and relevance.
Plan migration in phases: high-value active data first, historical data later, archive what is rarely used.
Define deduplication and conflict rules before migration. Validate data with real users after each phase. Keep legacy systems read-only during cutover to avoid drift.
Trust in data matters more than data volume.
Which security controls are typical for enterprise CRM?
Common enterprise CRM controls include:
- Role-based access and field-level permissions.
- Audit logs for critical actions.
- Encryption in transit and at rest.
- Data retention and deletion rules.
- Approval workflows for sensitive changes.
- Integration access controls.
- Monitoring and incident logging.
Security is designed into workflows, not added after deployment.
How to measure CRM ROI (KPIs)?
ROI measurement starts before implementation.
Effective KPIs usually cover:
- Customer retention and repeat sales.
- Deal velocity and conversion rates.
- Case resolution time.
- Workload distribution.
- Avoided costs such as churn or manual rework.
Each KPI must rely on CRM data and appear in real management decisions. ROI improves when metrics are reviewed continuously.
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us info@sumatosoft.com