IoT Design: How to Build, Principles, and Examples for 2026–2027
Key takeaways
- Holistic architecture: IoT design requires the seamless integration of 7 key components, ranging from physical sensors and network protocols to cloud infrastructure and user applications.
- The 2026 landscape: With over 21 billion connected devices, the focus has shifted from basic connectivity to solving complex challenges like regulatory compliance (EU Cyber Resilience Act), cross-vendor interoperability (Matter), and supply chain security.
- Strategic process: Building a successful solution follows a 4-step framework: detailed market research, ergonomic device engineering, robust architecture planning, and scalable fleet deployment.
- Core principles: Effective design relies on 9 pillars, including “security by design,” ensuring offline autonomy for devices, minimizing latency with edge gateways, and testing in real-world environments.
- Ethical imperative: Modern IoT design must prioritize user privacy and ethics, ensuring transparent data policies and protection against misuse in an era of constant surveillance.
We see IoT design in car-sharing and scooter-sharing services, fitness wearables, interconnected manufacturing systems, smart logistics with real-time tracking, autonomous warehouses, and more. These Internet of Things solutions are delivering benefits across industries.
Since 2012, SumatoSoft has closely followed and contributed to the evolution of IoT technology. We have implemented IoT solutions for our clients and continuously tracked industry developments. This technology has proven to be transformative in both business and daily life.
In this article, we define IoT design, outline the steps to build a successful IoT solution, highlight key design principles, and share examples of effective IoT implementations. To start, let’s briefly recap what the Internet of Things is.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things is the integration of the Internet and physical objects. The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers that can communicate with one another. Things are physical devices like sensors, smartphones, and fitness trackers. Combining these two terms yields the term Internet of Things, which refers to a network of physical devices.
An indispensable element of that term is the word “connected,” because an IoT system exists only when its devices (or IoT fleet) are connected to the Internet. If we disconnect and separate all devices, the IoT system ceases to exist and loses its benefits.
In the IoT context, we mean device connectivity: the more devices connected, the stronger the network.
The scale of IoT today is enormous. The world already has over 21 billion devices as of 2026. This number underscores that IoT is about much more than a handful of gadgets – it’s a complex ecosystem of devices, software, and services working together. See our article to learn more about why IoT matters.
However, IoT is not limited to devices. A complete IoT architecture typically comprises multiple layers and ecosystem components. Let’s look at the key elements that make up an IoT ecosystem.
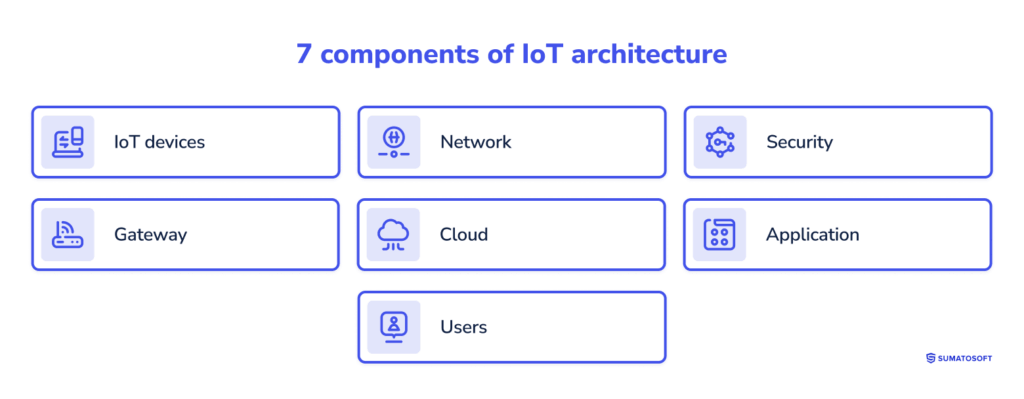
7 components of IoT architecture
The major components of the Internet of Things are:
- Devices
- Network
- Cloud
Keeping them in mind, you can build a simple IoT ecosystem. However, the more sophisticated the system you want to develop, the more components you will need.
If we look into the most featured IoT architecture, we find the following 7 components.
#1 component: IoT devices
Physical devices with sensors/actuators and network connectivity. These are the core elements that collect data (e.g., from the environment or user inputs) and can perform actions. IoT devices range from wearable fitness trackers and smart home appliances to industrial sensors and autonomous vehicles. They connect wirelessly (or sometimes via wired links) to an IoT network and transmit data over the Internet.
#2 component: Network
The communication network that connects all devices. This includes the protocols and infrastructure (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular 5G, LPWAN, mesh networks, etc.) that enable IoT devices to communicate with one another and with the cloud. The network serves as the glue between devices, allowing data transfer and remote control.
#3 component: Security
Measures and systems that ensure the IoT network and data are protected from unauthorized access and cyber threats. IoT security encompasses access control, encryption of data in transit and at rest, device and user authentication, and other protections. Robust security is critical for large enterprise IoT deployments (e.g., in industrial systems) and consumer IoT products, as breaches can lead to data leakage or unsafe conditions. User data privacy should also be a top priority.
#4 component: Gateway
An IoT gateway is a device or service that aggregates data from local IoT devices and connects them to the cloud (or to higher-level networks). It can be thought of as a “bridge” or gate between the device layer and the cloud layer. Gateways often perform protocol translation (so, for example, Bluetooth sensors can communicate with a Wi-Fi or cellular network via the gateway) and may do initial data processing or filtering at the edge to reduce latency and bandwidth usage.
#5 component: Cloud
The cloud (or other back-end infrastructure) serves as the “brain” of an IoT system. Cloud platforms provide large-scale data storage, processing, and analytics capabilities. The cloud is where raw sensor data is transformed into insights, often using big data analytics and machine learning (which is a part of AIoT development). With a robust cloud back end, IoT deployments can deliver advanced capabilities such as predictive maintenance, real-time alerts, and integration with enterprise systems. The cloud also hosts application logic and APIs that enable external applications or dashboards to interact with the IoT devices.
#6 component: Application
It is a graphical interface that enables users, business owners, employees, and others to communicate with an IoT system, manage its fleet, and check its status.
#7 component: Users
They are all people who influence the Internet of Things system and benefit from it.
With these components, you can describe any IoT system. However, knowing the structure is not everything. This is a theory, while you need mastery to design a high-quality IoT solution. Here we come to the term IoT design.
What is IoT design?
IoT design is the process of planning and developing every component of an IoT system with the technology’s unique requirements in mind. Traditional product design and software development methods often require adaptation for IoT, given the scale (potentially thousands of distributed devices), the need for real-time data handling, and the integration of physical and digital user experiences. In IoT design, one must consider all components from the hardware and network up through the cloud and applications to ensure they work together seamlessly.
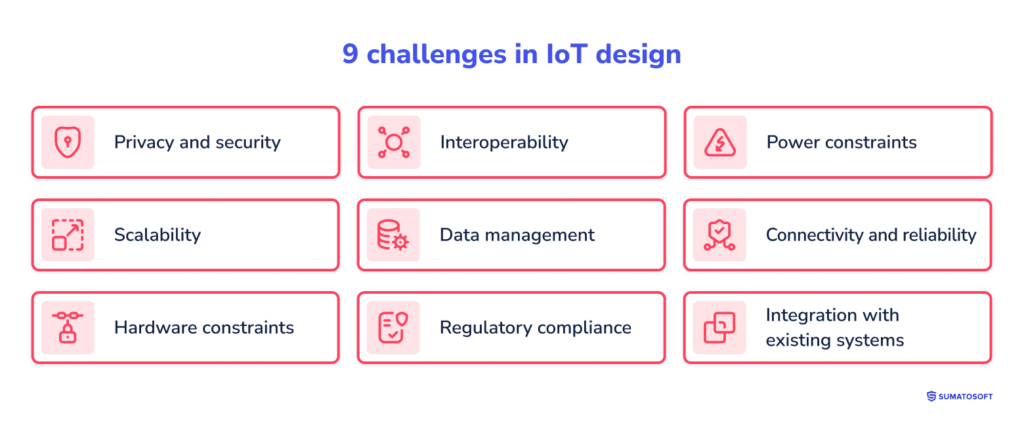
9 challenges in IoT design
Challenge #1: Privacy and security
IoT devices often collect vast amounts of data, including sensitive personal or operational information. This data must be protected during transmission and storage, and devices must be safeguarded against unauthorized access or tampering. A single weak link (like a poorly secured sensor) can open the door to hackers and data breaches. Strong encryption, authentication, and regular security updates are essential, but implementing them on resource-constrained devices can be challenging. Additionally, designers must follow privacy laws and obtain user consent to use data.
Challenge #2: Interoperability
IoT rarely starts as a multi-vendor ecosystem, but it becomes one. A pilot may run on a single stack; procurement adds another device line; and a partner brings their own gateway. Suddenly, you have a fleet that speaks incompatible protocols and data models. That is where interoperability stops being a “nice-to-have” and becomes a daily engineering task. Without a transparent integration layer with gateways, protocol bridges, and a standard device model, systems drift into silos, and teams waste time reconciling data instead of acting on it.
Challenge #3: Power constraints
Most IoT devices live on a strict energy budget. A sensor in a field or deep inside equipment cannot be charged every week, and “maintenance-free” becomes part of the product promise. Power management is a set of small decisions that add up. You reduce radio time, tune sleep cycles, compress payloads, and keep device-side compute lean. The outcome is higher sampling and richer data, which drains battery life, so the design must align with business needs rather than an ideal lab setup.
Challenge #4: Scalability
IoT projects look simple at the pilot scale. Then the fleet grows, and the same system that felt stable with twenty devices starts to break under two thousand. Scale impacts several layers simultaneously: message throughput, storage, dashboards, alert fatigue, and operations. If you cannot onboard devices fast, update firmware safely, and monitor device health with clear rules, you will spend more time firefighting than improving the product. That is why scalability is a cloud problem and an IoT operations issue.
Challenge #5: Data management
IoT data is a continuous stream that arrives daily from every device in the fleet. If you treat it as raw telemetry and store everything forever, costs rise while insight gets buried. Good IoT design starts with intent: which signals matter, which decisions depend on them, and what level of granularity is sufficient. From there, you build a data pipeline that filters noise, aggregates where possible, and uses edge processing to reduce load. The goal is data that leads to action.
Challenge #6: Connectivity and reliability
IoT systems operate in environments where networks are inherently imperfect: industrial sites, rural areas, moving vehicles, basements, and metal-heavy environments. Connectivity will drop, and it will do so at the worst time. Reliable IoT design assumes interruptions and plans around them: local buffering, retries, backoff logic, and clear offline behavior. The system should degrade predictably. Network choice is part of this: LPWAN fits some use cases, cellular fits others, and Wi-Fi is not a universal solution. The architecture has to match the operating environment.
Challenge #7: Hardware constraints
IoT hardware is shaped by limits: size, cost, power, and physical durability. That means you often work with small CPUs, limited RAM, and tight storage, while still needing secure communications and stable runtime behavior. These constraints force discipline in firmware and protocol choices. They also force realism about where computation belongs: heavy analytics moves to gateways or cloud services, while devices focus on sensing, basic validation, and safe control. At the same time, the device must survive heat, cold, moisture, dust, and vibration.
Challenge #8: Regulatory compliance
Regulation is now part of the IoT product surface. If you ship connected devices into different regions, you are designing a compliant product lifecycle. Privacy laws such as GDPR, sector rules like HIPAA, and radio or safety standards are already familiar. What is newer is how directly cybersecurity is being enforced for connected products. The EU Cyber Resilience Act adds expectations around secure development, vulnerability handling, and updateability, with obligations rolling in through 2026–2027. That changes planning: compliance cannot be patched in after launch, because it touches architecture, documentation, support, and the update process.
Challenge #9: Integration with existing systems
Most IoT deployments do not replace what a company already runs. They feed data into it. That means your IoT solution must work with ERP, CMMS, SCADA, data warehouses, identity systems, and ticketing tools, even if those systems were never designed for IoT volumes. Integration is where many projects lose time because it exposes mismatched data models, unclear ownership, and brittle interfaces. Strong IoT design treats integration as a first-class requirement: clear APIs, stable event schemas, mapping rules, and a plan for long-term maintenance. When that layer is done right, IoT becomes part of operations.
4 steps to proper IoT design
It would take an entire book to cover this topic. In that regard, we won’t go into describing the details of each step. Instead, we will help you gain a comprehensive understanding of Internet of Things design.
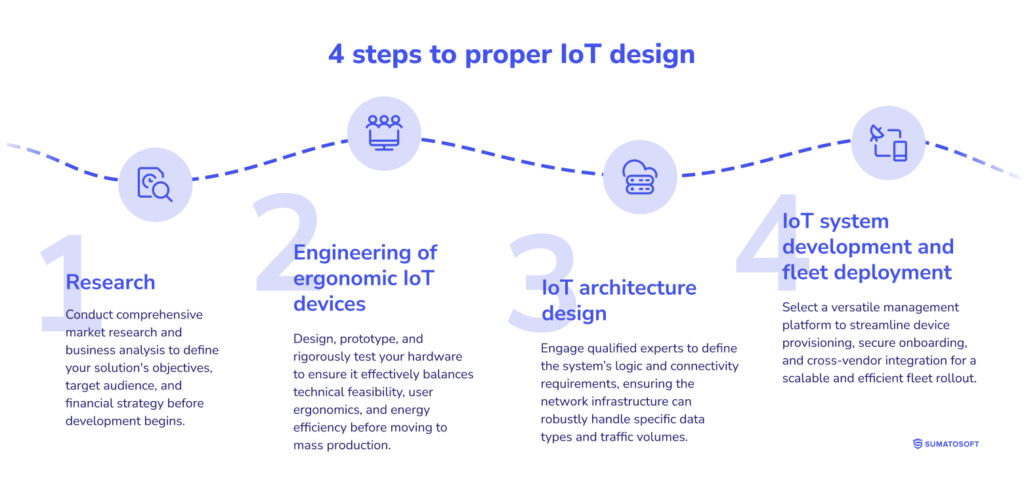
1st step: Research
The first step is a pre-development stage, where you identify challenges others face and understand how IoT can address them. This step is also called business analysis, discovery phase, market research, or conceptual stage. You need to understand what your future solution needs to address, identify the audience and how to reach them, create user profiles, define distribution channels, identify partners, draft a financial plan, and more. You also need to review the market and evaluate similar existing solutions. Consider yourself a startup that needs to pass the first startup development stage.
2nd step: Engineering of ergonomic IoT devices
An IoT fleet is the backbone of the network. You should carefully design, prototype, test, and construct the device before moving into mass production. It’s a complex journey, especially if you plan to use multiple types of sensors and actuators. A device for end users (such as fitness trackers) must be ergonomic and easy to use, while for industrial devices, one of the biggest challenges is battery life. It’s also necessary to find a reliable device vendor with sufficient experience in IoT fleet management and production.
In addition to all the above, you need to understand whether your solution is possible to build using IoT devices. IoT affects various industries, and devices in some industries, like healthcare are very complicated since their accuracy must be close to 100%, and interruptions in operation can lead to people’s death, so it requires a lot of financing and expertise. On the other side, if your idea is connected with smart homes, it will be much easier to find a device manufacturer or build a device on your own. Balance your desires with possibilities.
3d step: IoT architecture design
To build an IoT architecture, you can use the services of specialized companies like SumatoSoft or hire a highly qualified IoT architect. Whatever you choose, keep in mind that this step is critical and you shouldn’t compromise on it. System logic and key elements of the entire IoT ecosystem are defined here. Pay special attention to network characteristics and technologies, as they must handle the traffic volume they carry. Define the types of data it will transmit, including voice, video, images, and text. Dealing with IoT traffic requires specific network requirements.
4th step: IoT system development and fleet deployment
When the IoT fleet is ready to deploy, you’ll require a comprehensive system to manage it. Using specialized platforms is the best way to develop such a system. When choosing a platform provider, you should examine the technologies they support, the ability to register devices from different vendors that use other protocols, and the platform’s pricing.
Before the fleet deployment, you need to create an instance for each device in the system, record device information, provide secure housing for each device, set up permissions and access rights, and more. Device onboarding can be challenging without the right IoT fleet management platform. The right platform can increase production throughput and help achieve a fourfold increase in device provisioning.
Best IoT platforms in 2026: what to use and when
Smart home ecosystems (consumer IoT)
- Apple Home (HomeKit) – for iOS-first smart home devices and Home app integration.
- Google Home ecosystem – for Android-first smart home products and broad consumer reach.
- Amazon Alexa ecosystem – for voice-first smart home use cases and device compatibility.
- Matter (standard, not a platform) – when you need cross-ecosystem device interoperability (Apple/Google/Amazon).
Cloud IoT platforms (device connectivity + fleet management)
- AWS IoT (Core + Device Management) – for large-scale device fleets, strong cloud integration, and flexible architectures.
- Microsoft Azure IoT (IoT Hub + DPS + IoT Edge) – if your stack is already Microsoft-heavy and you need robust device provisioning and edge support.
Industrial and enterprise IoT platforms (IIoT)
- PTC ThingWorx – for industrial IoT apps where you need rapid delivery of dashboards, workflows, and connectors.
- Siemens Insights Hub (ex-MindSphere) – for manufacturing environments and Siemens-centric industrial ecosystems.
In case you work with the mass market, an additional step here is building a fast and user-friendly application. The application development lifecycle consists of designing and prototyping, programming, testing, and releasing the application.
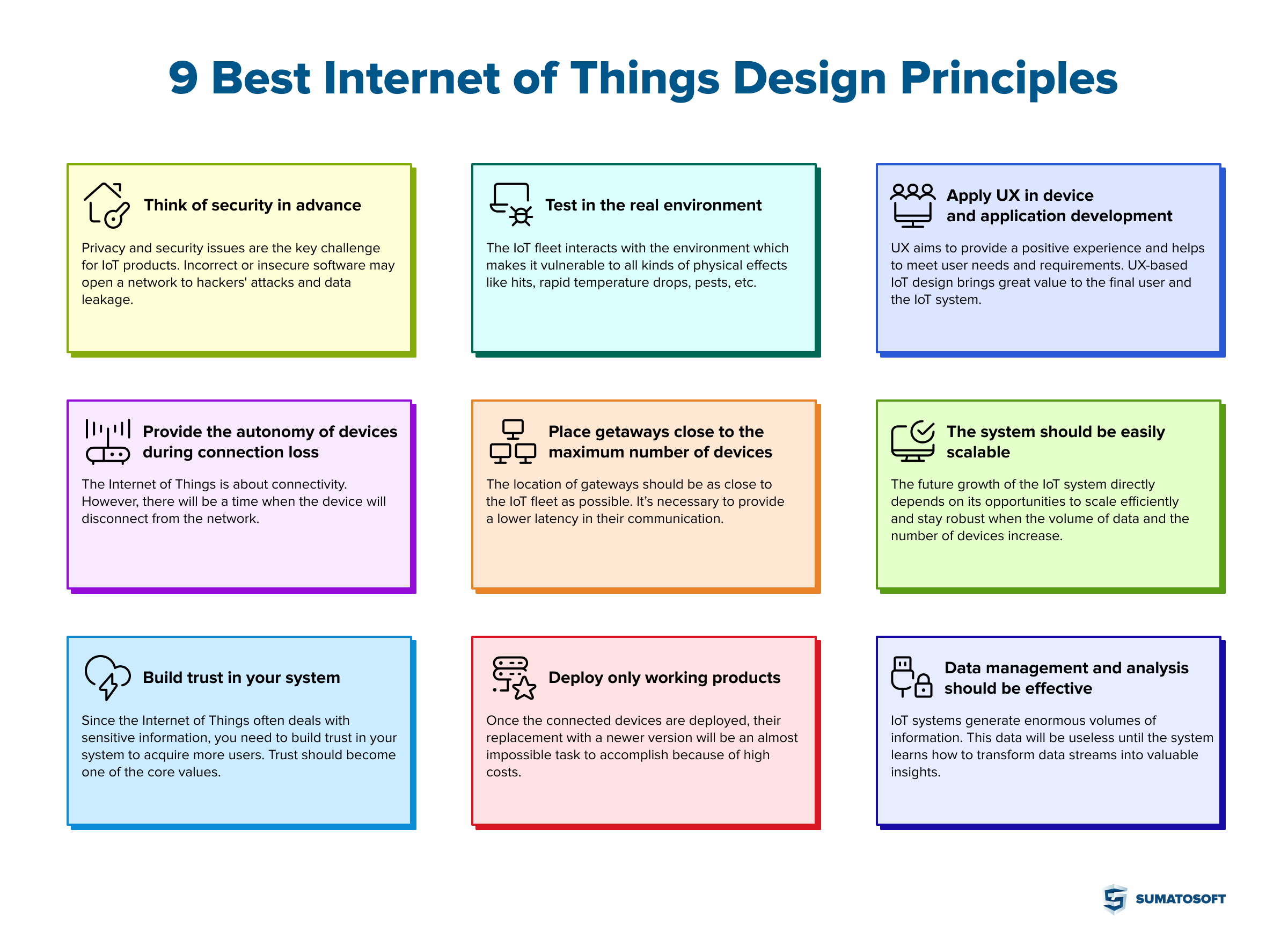
9 best IoT design principles
#1 principle: Think of security in advance
Privacy and security issues are the key challenge for IoT products. Incorrect or insecure software may open a network to hackers’ attacks and data leakage. In addition, there is a need to establish proper security update processes as a part of IoT update management to deploy security patches effectively and quickly.
#2 principle: Test in the real environment
The IoT fleet interacts with the environment which makes it vulnerable to all kinds of physical effects like hits, rapid temperature drops, pests, etc. All these treats are hard to test in laboratory conditions, so it’s necessary to test devices in a real environment where they are supposed to work further.
#3 principle: Apply UX in device and IoT application development
UX aims to provide a positive experience and helps to meet user needs and requirements. UX-based IoT design brings great value to the final user and the IoT system.
#4 principle: Provide the autonomy of devices during connection loss
The Internet of Things is about connectivity. However, there will be a time when the device will disconnect from the network. The device should continue to work properly and transfer the collected information when the connection will be restored.
#5 principle: Place getaways close to the maximum number of devices
The location of gateways should be as close to the IoT fleet as possible. It’s necessary to provide a lower latency in their communication.
#6 principle: The system should be easily scalable
The future growth of the IoT system directly depends on its opportunities to scale efficiently and stay robust when the volume of data and the number of devices increase.
#7 principle: Build trust in your system
Since the Internet of Things often deals with sensitive information, you need to build trust in your system to acquire more users. Trust should become one of the core values.
#8 principle: Deploy only working products
Once the connected devices are deployed, their replacement with a newer version will be an almost impossible task to accomplish because of high costs. That means that one single error in the fleet which is detected after the fleet deployment can lead to large financial losses. Due to that, it’s good to avoid untested hardware iterations and deploy only working products.
#9 principle: Data management and analysis should be effective
IoT systems generate enormous volumes of information. This data will be useless until the system learns how to transform data streams into valuable insights. It is up to effective data management and analysis whether the IoT system will generate value or just become a data warehouse.
The significance of the ethical aspect in IoT design
As IoT devices and applications become more prevalent, it’s essential to consider the ethical implications of IoT design. Some key ethical considerations include privacy, security, data ownership, and transparency.
For example, imagine a smart home security system using cameras and sensors to monitor a family’s activity. While the system may be effective at preventing theft or intruders, it could also collect personal data on the family’s daily routines and habits, which could be used for malicious purposes if it falls into the wrong hands.
How IoT engineers can address this issue:
Implement security controls: IoT designers should implement encryption and authentication to protect user data from unauthorized access.
Develop transparent data policies: IoT designers should establish policies that clearly explain what data is collected and how it will be used, and obtain user consent before collecting any personal data.
Consider the impact on vulnerable populations: IoT designers should assess the potential consequences of their designs, particularly for children, older adults, and people with disabilities, and work to ensure their products are accessible and inclusive for all users.
Prioritize privacy by design: IoT designers should incorporate privacy considerations into the design process from the outset, rather than as an afterthought.
Educate users: IoT designers should provide clear, concise instructions for using their products safely and securely, and offer resources to help users learn more about IoT security and privacy best practices.
Great IoT design examples
Tractive: Comprehensive monitoring and lifecycle management
Tractive successfully addresses the challenge of pet tracking by combining real-time GPS monitoring with health analytics in a single unified application. The system processes raw sensor data to generate actionable insights for pet owners.
However, this case also illustrates the critical importance of lifecycle planning in IoT. Following Tractive’s acquisition of its competitor, Whistle, the latter’s platform was discontinued. On August 31, 2025, all Whistle devices ceased functioning. This serves as a stark reminder that in the IoT sector, physical hardware is reliant on the continued operation of its underlying cloud service.
Philips Hue: Stable interoperability via Matter
Smart lighting systems often encounter compatibility issues when integrating devices from different vendors. Philips Hue addresses this through the Hue Bridge, which acts as a stable central hub. With support for the Matter standard, the system ensures seamless interoperability with other ecosystems. This approach simplifies setup and allows users to scale their smart home infrastructure without complex network reconfiguration.
August Wi-Fi Smart Lock: Security and access control
The August Wi-Fi Smart Lock establishes user trust through transparent security features, including mandatory two-factor authentication, data encryption, and detailed activity logs. The product is designed for practical application, offering flexible guest access management and integration with voice assistants. It represents a device that successfully balances rigorous security protocols with everyday usability.
Final words from SumatoSoft
The Internet of Things has matured from an emerging trend into a fundamental business technology. However, raw connectivity alone is insufficient. Successful implementation requires a disciplined design approach.
IoT design applies structured principles to complex, multi-device ecosystems, ensuring that unique architectures translate into reliable performance and a coherent user experience. We’ve been working with the Internet of Things technology since 2012 and have accumulated expertise and experience in building comprehensive enterprise software. We also help startups with MVP software development.
Contact us for a consultation about your project!
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us info@sumatosoft.com